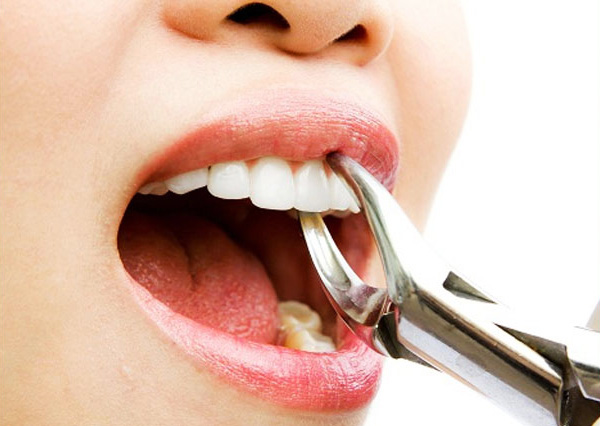
Tooth extraction is the removal of a tooth from its socket in the jawbone. This procedure is typically done by a dentist or oral surgeon, and it may be necessary for a variety of reasons, such as:
Some common pediatric dental treatments include:
- Severe tooth decay that cannot be repaired with a filling or crown.
- Advanced gum disease that has caused the tooth to become loose.
- A crowded mouth where a tooth cannot emerge properly
- A damaged or broken tooth that cannot be repaired
- In preparation for orthodontic treatment
The tooth extraction procedure typically involves the following steps:
Pediatric dentists also provide education and guidance to parents and children about proper oral hygiene and diet to maintain healthy teeth and gums.
- Anesthesia: The area around the tooth will be numbed using a local anesthetic to ensure that the procedure is painless.
- Tooth removal: The dentist or oral surgeon will use specialized tools to gently loosen the tooth from its socket and remove it.
- Post-operative care: After the tooth has been extracted, gauze will be placed over the extraction site to control bleeding. The patient will be instructed to bite down on the gauze for a period of time to allow a blood clot to form. The dentist may also prescribe pain medication or antibiotics to prevent infection.
- Follow-up appointment: The patient will be asked to return for a follow-up appointment to ensure that the extraction site is healing properly.
It is important to follow the dentist's instructions for post-operative care to prevent complications and ensure a speedy recovery. The patient should avoid eating hard or crunchy foods, smoking, or drinking through a straw for at least 24 hours after the procedure.
